Setting up a VLAN on your network? Here are the things you need to know before getting started.

Security is one of the biggest concerns in 2025; many people online are simply sitting there trying to hijack your data. While you might be a tech enthusiast, knowing a lot about build configs, you cannot likely monitor every packet your PC exchanges across the Internet. People with ill motives can do many sinister things if they get access to your PC, via tunneling methods, or by getting in through browser exploits. VLANs won’t completely prevent intrusion, but they can significantly limit bidirectional traffic movement within your network. To fully lock down your network, your VLANs should be paired with a firewall and an access control list (ACL) configuration.
Note: This article is aimed at tech-savvy readers. It gets very technical after a while as it explores VLAN security practices, common drawbacks, and more.
Understanding VLANs and Their Core Benefits
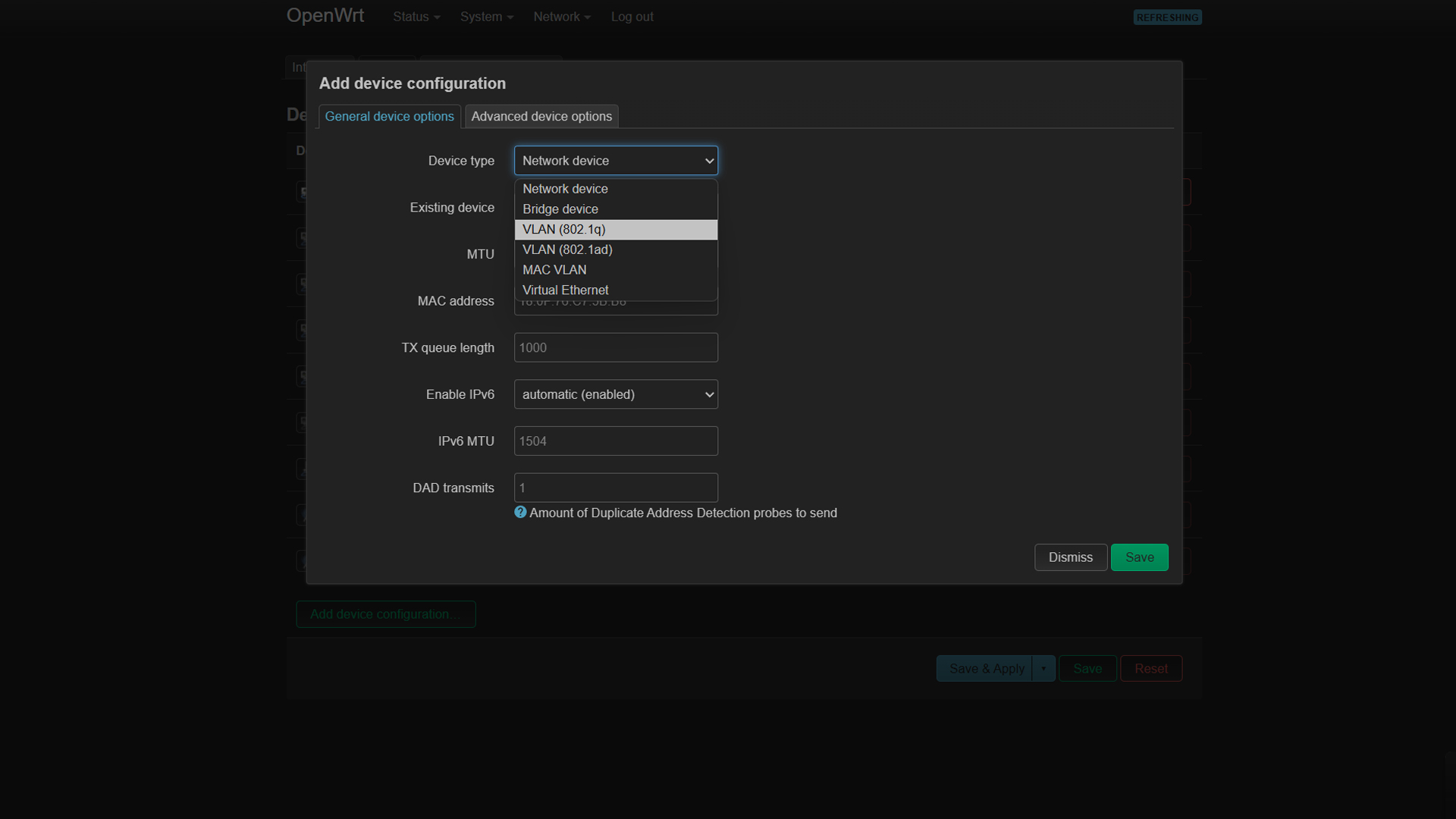
VLAN, or Virtual Local Area Network, is fundamentally a logical grouping of devices connected to a single Ethernet. Put simply, you group five devices connected to your router as one network. VLANs’ greatest benefit is reducing broadcast domains per network device and subnets. Rather than requiring separate physical network hardware for different network zones, VLANs allow multiple networks to share the same physical connection without interference.
Take a practical example. Let’s say you use a router with VLAN support (e.g., pfSense, MikroTik, or even some high-end consumer routers). With VLANs, a single physical switch or Wi-Fi access point can act like several isolated networks. Your work laptop, IoT devices, and gaming rig can be segmented into separate VLANs, keeping risky or noisy traffic isolated.
Note: VLANs don’t inherently add latency, but cheap or underpowered routers/switches can bottleneck with 10+ VLANs, primarily if Layer 3 routing or inter-VLAN ACLs are used.
Advantages of VLANs in 2025
Now that the basic understanding is clear, VLANs are more than just a cool networking term. The main reason they are used is the level of security they provide. Once you set up VLANs correctly, attackers will still get in, but as discussed earlier, you need a strong firewall with ACLs.
Here’s what makes VLANs worth it:
- Security Through Segmentation: VLANs isolate devices into separate groups. If one device is compromised, others stay unaffected unless explicitly connected or have a tunneling pathway exposed.
- Simplified Network Management: Users can move physically without changing configs. Just assign them to the correct VLAN, and you are ready.
- Broadcast Traffic Containment: Devices only hear what’s meant for their VLAN. Less noise means more efficient traffic, which, as discussed earlier, saves a lot of broadcast domain assignments.
- Stronger Access Controls: VLANs allow you to isolate network zones, such as guest traffic from employee systems or dev environments from production.
Setup and Planning

Before diving in and starting to group devices, you must map out your setup.
- Start with a Network Diagram: Sketch all switches, routers, and connections. Cisco Packet Tracer or GS3 is an excellent software for this plan. Before getting into it, you can virtually emulate VLANs in this software itself.
- Group Logically: Consider who needs access to what, such as teams, roles, and services.
- Design for Growth: Leave gaps in your VLAN ID scheme (e.g., use VLAN 10, 20, 30) to add new groups later without the hassle of renumbering.
After you finish the planning process, security comes next. Below are a few best practices that you should follow.
- Never Use VLAN 1: It’s the default and a favorite target. Disable or blackhole it.
- Change the Native VLAN: Avoid mismatches and keep native VLANs away from user VLANs.
- Create a Management VLAN: Isolate switch/router management traffic so regular or even guest users can’t access it.
- Lock Down Unused Ports: Dispose of unused ports into a random empty VLAN with no DHCP or routing. This will reduce your network’s exposure and give you fewer headaches.
Configuring VLANs: Access vs. Trunk
After you finish your planning phase, it’s time to understand how traffic will flow. There are multiple methods for this. Below are a few guidelines.
- Access Ports: Uses one VLAN only. Perfect for most end-user devices.
- Trunk Ports Carry traffic for multiple VLANs (tagged). They are used for switch-to-switch or switch-to-router connections. VLAN tagging ensures devices stay in their lane. Each packet includes a 12-bit header for this purpose.
Mistakes to Avoid
It’s very easy to get things wrong, as the entire process is complicated to execute simultaneously. You can consider a few points while doing it, such as:
- Pay close attention to VLAN IDs; mismatching will cause your network to drop.
- If you are on a budget, consider keeping the connections list short, as too many devices will strain your switch/router.
Note: When stacking VLANs on a port, 802.1Q handles dozens/hundreds of VLANs per trunk just fine, as long as traffic isn’t saturating the link.
Prepping for Troubleshooting
You will likely run into issues, as VLAN is one of the more complex topics in networking. Worry not; the following is a good starting point, provided you are doing this on the CLI and do not have GUI-based guides.
- Use Show Commands like ‘show interfaces trunk‘ or ‘running-config’ to reveal misconfigured ports. (You can also do this in Packet Tracer.)
- Look for VLAN Mismatches: These can cause traffic leaks or silent failures.
- Keep VTP Modes Consistent: Misaligned modes can wipe out your VLANs, destroying all your work.
- Monitor ACLs: Don’t block what should be allowed, or vice versa.
Conclusion
In conclusion, VLANs offer incredible security and network segmentation on a home or office network. But remember, setting them up correctly requires a lot of work, followed by maintenance. Always know what you are doing here. Setting them up with clear goals will make your network stronger, more efficient, and safer.
Looking For More Related to Tech?
We provide the latest news and “How To’s” for Tech content. Meanwhile, you can check out the following articles related to PC GPUs, CPU and GPU comparisons, mobile phones, and more:
- 5 Best Air Coolers for CPUs in 2025
- ASUS TUF Gaming F16 Release Date, Specifications, Price, and More
- iPhone 16e vs iPhone SE (3rd Gen): Which One To Buy in 2025?
- Powerbeats Pro 2 vs AirPods Pro 2: Which One To Get in 2025
- RTX 5070 Ti vs. RTX 4070 Super: Specs, Price and More Compared
- Windows 11: How To Disable Lock Screen Widgets
 Reddit
Reddit
 Email
Email