Learn how to reduce Input Lag in online games by tweaking monitor settings, GPU performance settings, and more.
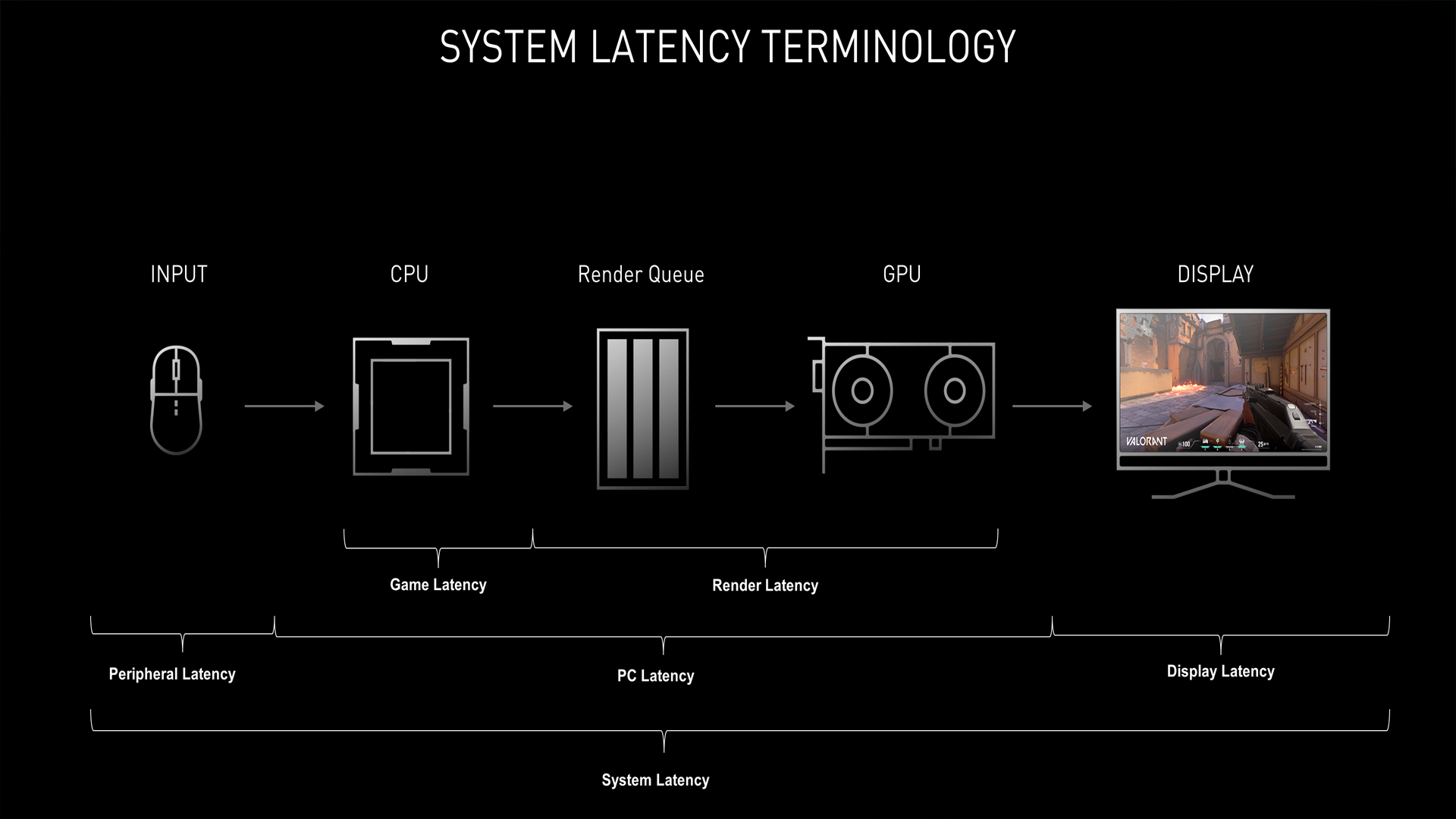
Have you ever felt that your inputs are taking longer to appear on your screen? This is because you are experiencing input lag issues. Input lag is the delay between your actions and their appearance on your computer’s screen. In terms of competitive gaming, this input lag can significantly impact the outcome of your match. Everything from the build quality of components, your internet connection, processor, RAM speeds and timings, motherboard, and network card can contribute to input lag.
Hardware combinations can be infinite, and there is no single fix to resolve this issue entirely. However, today’s article discusses methods that reduce this to some extent.
Reducing Input Lag in Online Games
Below are a few steps you can take to fix your input latency. Remember, to fix this problem, at the very base level, you need to check your Internet connection — that’s where most of this problem lies. It’s not a regular speed test; rather, the process is quite complex.
In short, you need to:
- Find the game server IP.
- Run a traceroute.
- Check for packet loss.
If you have packet loss, there’s your answer. Otherwise, if there’s still no packet loss, but the ping is a bit on the higher side (ask your friends how much ping they get), consider trying another ISP as a trial and see how it fares. If the input problem is solved, then and there — congrats, you’ve permanently found a solution. If not, try the ones mentioned below, as it could be something else causing the issue.
Monitor Settings
- Set your monitor to its highest refresh rate (e.g., 144Hz or 240Hz)
- Enable “Game Mode” on your monitor to bypass any extra technical features, such as color processing.
- Use a gaming monitor with low response time; OLED is the best here.
- Connect your monitor directly to your graphics card using DisplayPort or HDMI. (Sometimes on laptops, the HDMI port is IGP-bound, and this adds latency.)
GPU & Graphics Settings
- Disable V-Sync in games and the GPU control panel; V-Sync is notorious for adding extra input latency.
- Use adaptive sync instead (G-SYNC, FreeSync, or Intel Adaptive Sync) for smooth gameplay without additional delay. Or use nothing at all if none of these techs are available to you.
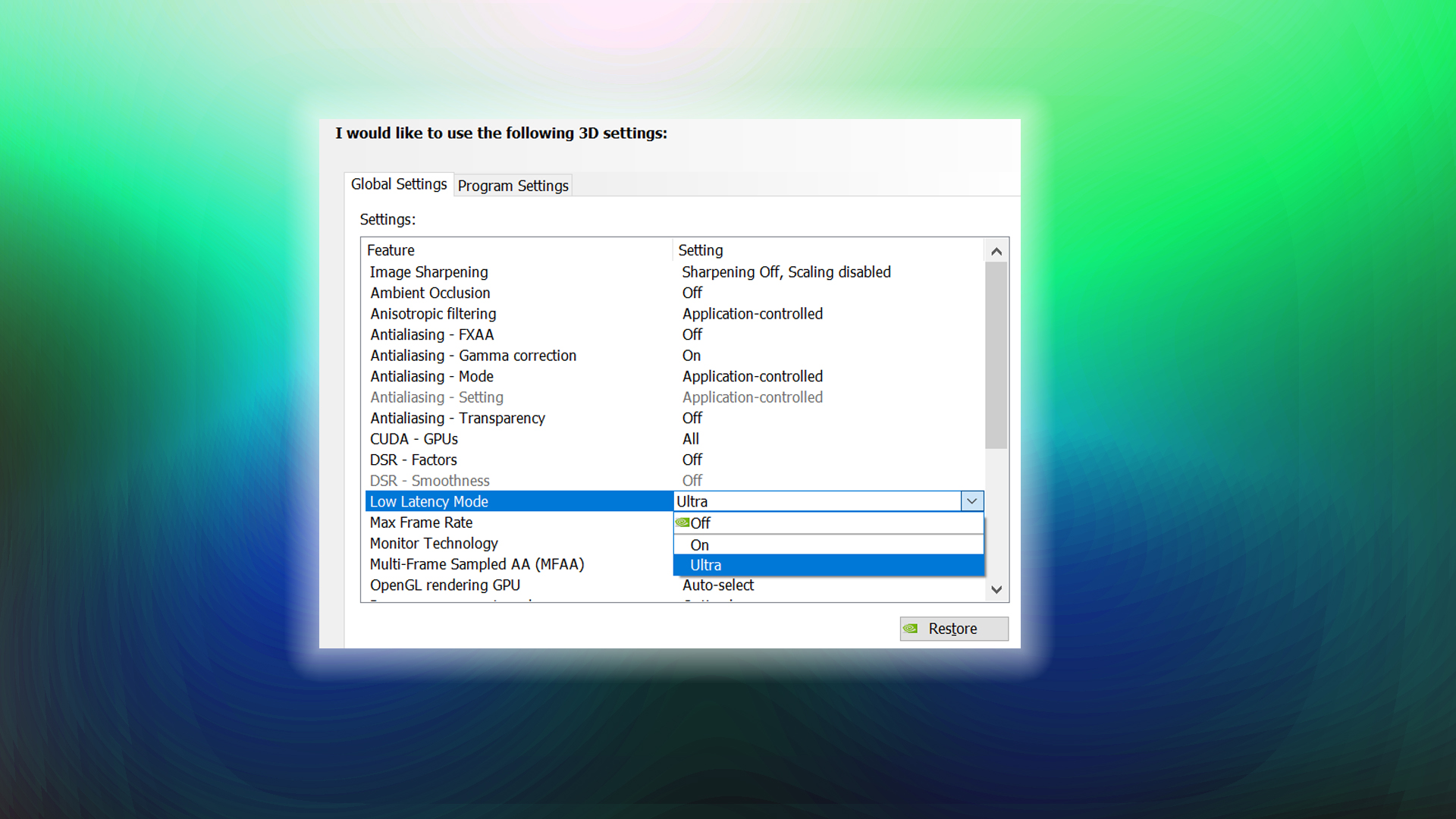
- For NVIDIA GPUs, enable “Ultra Low Latency Mode” in the NVIDIA Control Panel. For AMD, enable “Anti-Lag” and input delay reduction.
- Lower graphics settings (resolution, effects) to reduce GPU load and achieve high FPS figures.
- Set “Maximum Pre-Rendered Frames” (NVIDIA) or “Flip Queue Size” (AMD) to 1 to minimize frame buffering.
- Cap your FPS just below your monitor’s refresh rate to reduce GPU usage, which improves your system’s latency. The ideal figure is 95-97% GPU usage.
- On supported games, utilize NVIDIA Reflex to reduce input latency significantly.
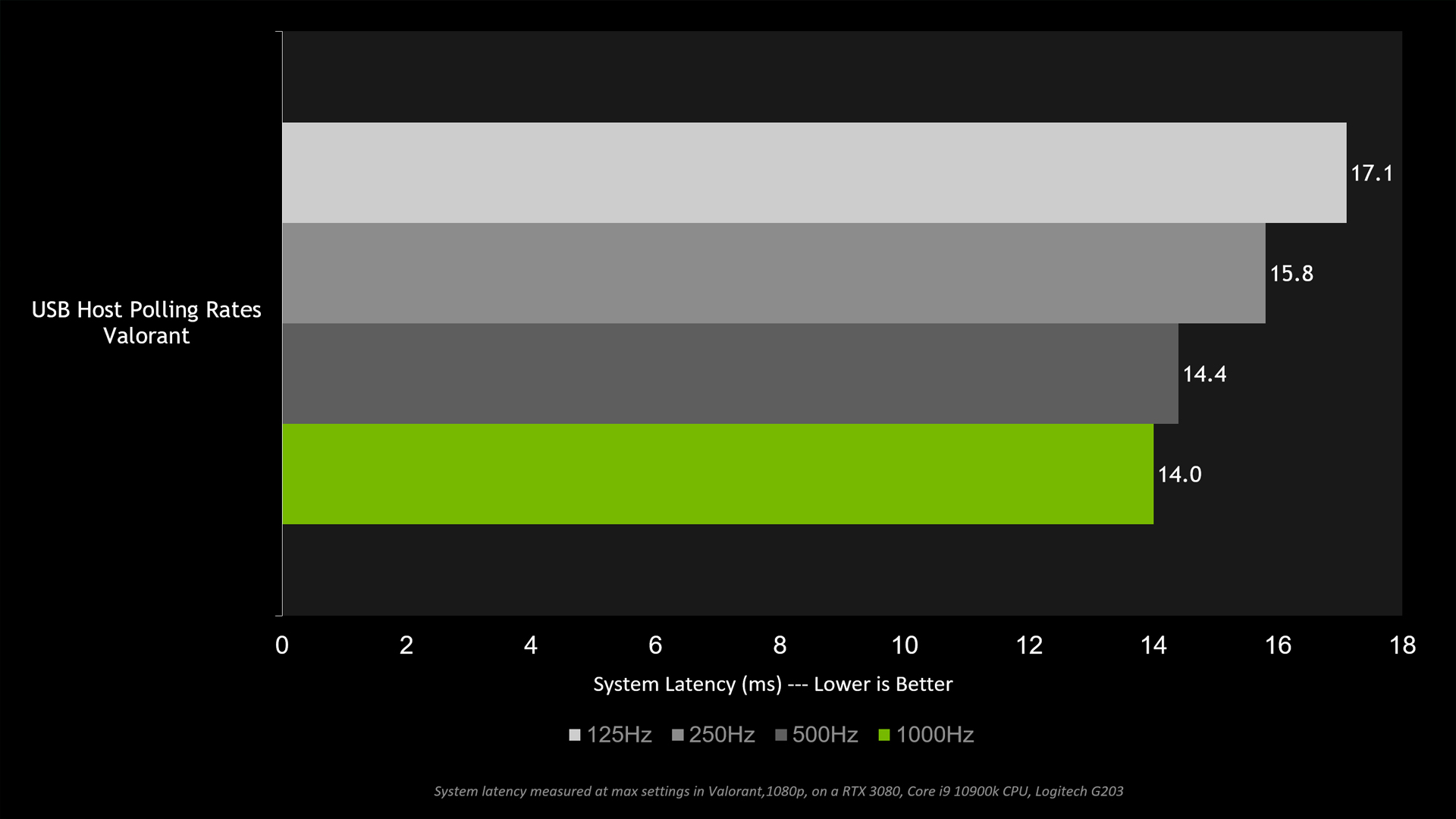
- Ensure your mouse is on the highest polling rate that it can offer.
System & Peripheral Tweaks
- Disable HPET(High Precision Event Timer) from the device manager
- Keep graphics, chipset, and peripheral drivers up to date.
- Set your PC to “High Performance” mode and disable power-saving features.
Conclusion
It is important to note that on the Intel platform — especially 11th Gen and above — you can expect a lot of input latency, simply because the CPU’s architecture differs from the golden dual-ring bus found on the 10th Gen Core i9-10900K. Some rumors suggest that Intel has shifted the I/O controller over to the motherboard, which is the biggest reason why this input latency issue is so frustrating. Additionally, there are oxidation issues and other concerns.
On AMD, as of now, the 7000 Series and above also experience latency issues; however, these have been mitigated to a large extent by the recent AGESA improvements delivered through BIOS updates.
We provide the latest news and “How To’s” for Tech content. Meanwhile, you can check out the following articles related to PC GPUs, CPU and GPU comparisons, mobile phones, and more:
- 5 Best Air Coolers for CPUs in 2025
- ASUS TUF Gaming F16 Release Date, Specifications, Price, and More
- iPhone 16e vs iPhone SE (3rd Gen): Which One To Buy in 2025?
- Powerbeats Pro 2 vs AirPods Pro 2: Which One To Get in 2025
- RTX 5070 Ti vs. RTX 4070 Super: Specs, Price and More Compared
- Windows 11: How To Disable Lock Screen Widgets
 Reddit
Reddit
 Email
Email


