Find out ways in which undervolting your GPU can help your gaming laptop with extended battery life, lower temperatures, and more.
Gaming laptops nowadays are incredibly powerful due to manufacturers providing high-performance CPU and GPU models inside them. Meanwhile, laptop coolers have undergone a significant evolution. Still, modern processors and laptop chips have very high transistor counts, and within a short space, they are incredibly hard to cool.
This is plain physics in action. If the source of heat is large, then it’s easier to cool; whereas if it’s tiny and produces immense heat, then cooling becomes seriously complicated. This is where undervolting shines, particularly for the GPU, as it is the component that consumes the most power from your laptop’s budget. Let’s dig in.
How Undervolting Works

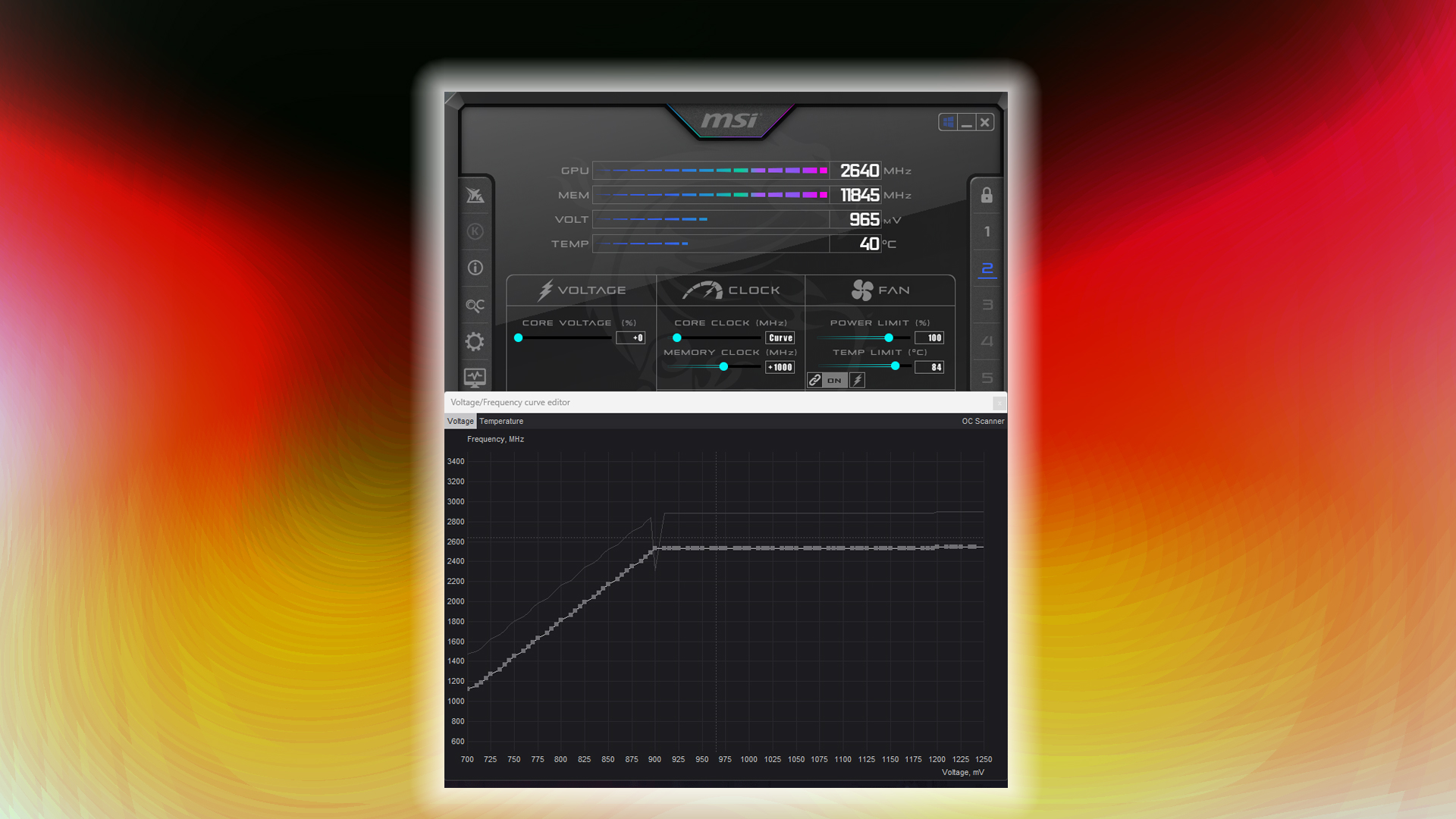
Due to stability concerns, every laptop manufacturer and GPU vendor determines a voltage-to-frequency curve that is generally on the higher side, sufficient to sustain the advertised clock speed.
However, many GPUs, depending on their binning, can reach the advertised frequency at a much lower voltage, which creates a significant drawback for this approach. If you undervolt your laptop’s GPU, the power draw decreases by around 10-25%. Your CPU, depending on how the BIOS is configured, can efficiently utilize this remaining power.
Now, here is the fun part: once you find that your laptop’s GPU can reach its advertised frequency at a lower voltage, you can gradually increase the clock speed until it becomes unstable at that voltage.
Once you find the sweet spot, like frequency to voltage to power, you can call it a day. Alternatively, if you want to push further, slowly increase the voltage and observe its stability. This way, you are maximizing your laptop’s TGP, since you cannot raise it without shunt-modding. Games will notice improved performance, of course, depending on the game and whether it is core-heavy or memory-heavy.
Key Benefits
As discussed earlier, here are some key benefits that follow after an undervolt.
- Extended battery life
- Lower temperature and noise
- More sustained peak performance
- Better lifespan of components due to lower heat
Potential Downsides
An overly aggressive undervolt can cause stability issues and may produce graphical glitches and artifacts within the 3D workload. It is best to check out review outlets and get an estimate of how things are, and then proceed very cautiously.
Performance does fall off when you are undervolting, regardless of whether you are hitting the same frequency; it drops by 2-3%. However, this can be mitigated by increasing the VRAM clock.
Verdict
On PCs, this process is easily carried out by MSI Afterburner or any other GPU vendor software. However, in laptops, many models, such as those from Lenovo, MSI, Clevo, and Asus, offer control panels that allow you to perform steps like this, and even in a more simplified manner than using a curve editor approach.
That said, if you are running into thermal constraints, undervolting can turn things around; it’s a very low-risk and high-reward option you can try out, as undervolting doesn’t brick your hardware, whereas overvolting does.
We provide the latest news and “How To’s” for Tech content. Meanwhile, you can check out the following articles related to PC GPUs, CPU and GPU comparisons, mobile phones, and more:
- 5 Best Air Coolers for CPUs in 2025
- ASUS TUF Gaming F16 Release Date, Specifications, Price, and More
- iPhone 16e vs iPhone SE (3rd Gen): Which One To Buy in 2025?
- Powerbeats Pro 2 vs AirPods Pro 2: Which One To Get in 2025
- RTX 5070 Ti vs. RTX 4070 Super: Specs, Price and More Compared
- Windows 11: How To Disable Lock Screen Widgets
 Reddit
Reddit
 Email
Email


