Here is everything you need to know about the inner workings of RTX 50 Series GPUs including DLSS 4, Multi-frame Gen, and Reflex 2.

With the release of the RTX 50 Series cards, Nvidia aims to put a powerful set of GPUs on the market. Gamers and creatives are looking forward to enjoying massive performance gains while using these cards. However, true native performance gains seem to be roughly between 20% and 35%, depending on the card. Naturally, people are questioning whether it is worth springing for a brand-new graphics card for such gains in performance.
There is more to the RTX 50 Series GPUs than just raw specifications, which makes them special. DLSS 4 is one of the latest upscaling technologies introduced by Nvidia. They aim to bring DLSS 4 to the RTX 50 Series lineup before other compatible GPUs. It certainly begs the question: does DLSS 4 make the RTX 50 Series worth buying? Let us find out.
How Did Nvidia Make the RTX 50 Series More Powerful?
As we approach a vital pivot in gaming technology, the way to increase performance outputs in GPUs is typically to make space to fit more transistors. This is usually done by shrinking the chips to fit them with more transistors. However, as time passes, it’s becoming harder and more expensive to shrink the chips. Nvidia has employed a new approach here.
With the RTX 50 Series, Nvidia has decided to emphasize its efforts on AI more. Therefore, it’s AI that is responsible for the framerate leaps that are expected from this latest GPU lineup. Rather than hardware, it’s the software that is producing framerate boosts via AI.
DLSS 4: All You Need To Know
From 2020 onwards, DLSS has been an integral part of Nvidia’s graphic cards. Over the years, Nvidia has upgraded the DLSS technology by moving to a more complex upscaling model. Looking at the results produced by DLSS, most would agree that it is the best upscaler. However, it is still far from perfect. In certain scenarios, it is rather easy to spot reduced image quality and ghosting. The same scenarios show improved image quality when tested while using the new upscaling models employed by DLSS 4.
More than 80% of RTX graphics card owners are using DLSS, according to Nvidia reports, while the technology now supports 540 games and applications. Artificial intelligence technology benefits from continuous training because it produces enhanced performance and quality improvements over time. DLSS started with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) as its modeling foundation before Nvidia implemented transformers for its latest update.
Transformers served as a fundamental component for numerous advanced AI developments over the past two years, which have produced complex applications, including AI image generation and text generation.
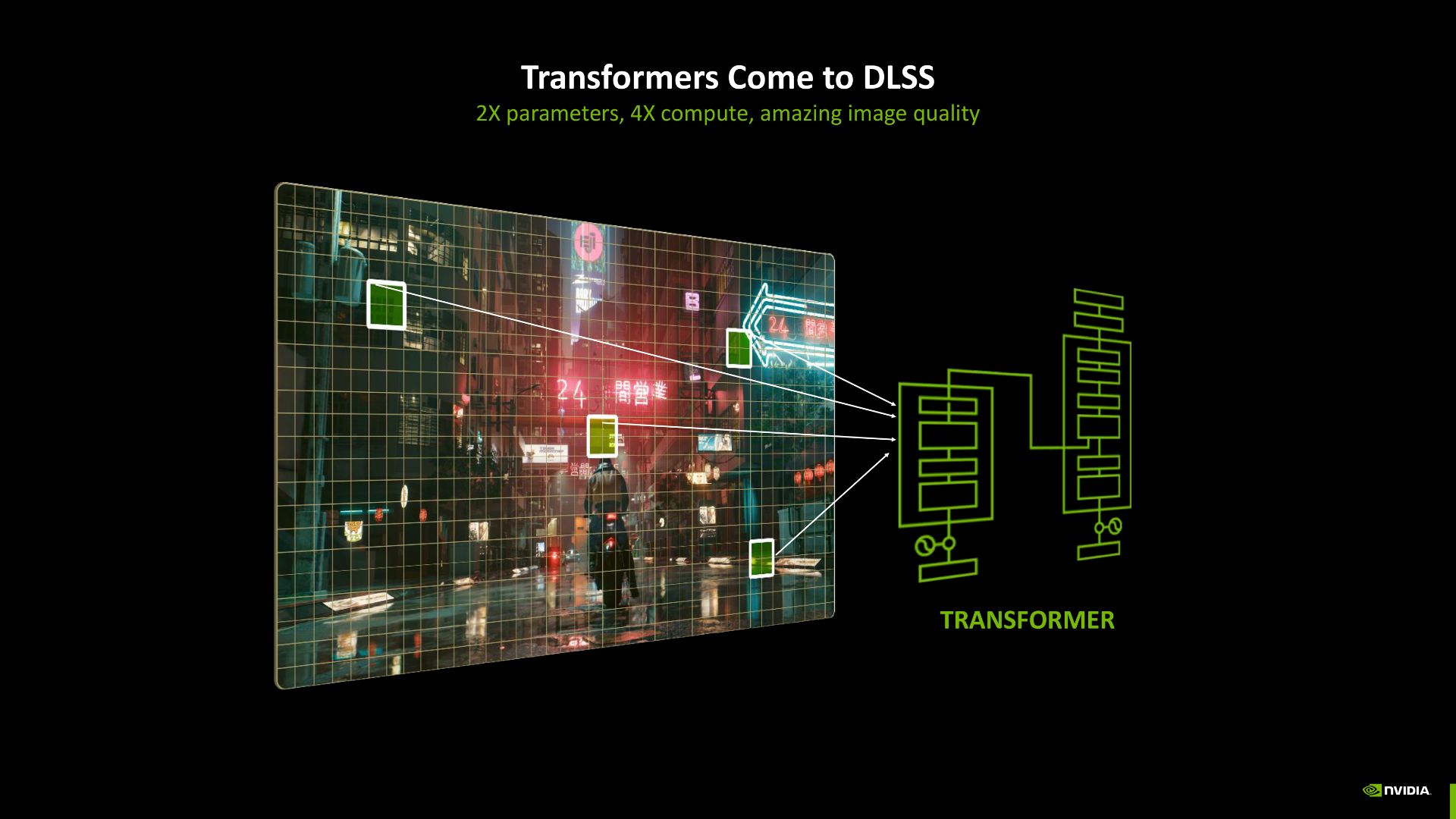
Nvidia achieved superior image quality by implementing their new DLSS transformer model, which increased parameters by two times and needed four times the computational power. At the time of RTX 50-series release, gamers will benefit from accessing DLSS adjustment settings through the Nvidia App across at least 75 compatible titles.
DLSS transformer models require additional computational power that reduces their frame rate performance, notably on older RTX GPUs. The new models could enable DLSS Performance mode upscaling at 4X resolution that delivers improved visual quality compared to DLSS CNN Quality mode upscaling at 2X resolution.


These pictures demonstrate how DLSS transformers improve visuals in Alan Wake 2 and Horizon Forbidden West. The new ray tracing system in Alan Wake 2 delivers ray reconstruction for improved visuals at faster performance speeds than previous CNN models. The upscaling ability in Forbidden West attained peak performance to show off improved detail quantity.
The early footage alongside images indicates that DLSS has reached a quality standard that is better than native one, after multiple years of polarizing expectations. Each game delivers distinct results with this enhancement but users with any RTX GPU can now access it.
Multi-Frame Generation Explained
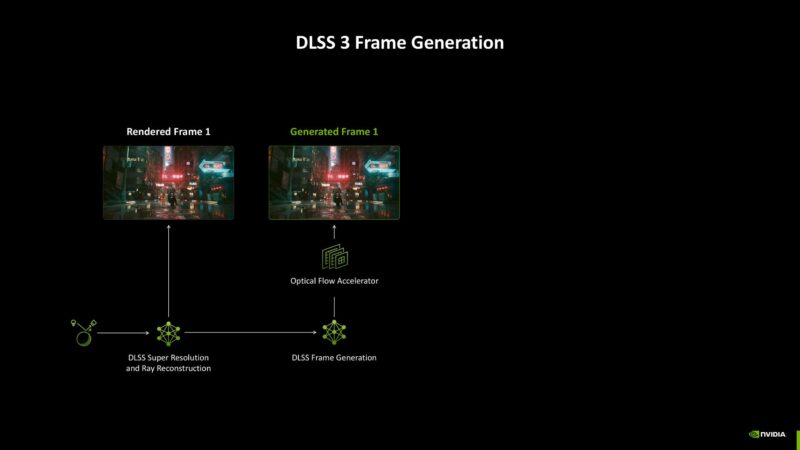
Multi-frame generation is another grand reveal by Nvidia, a technology exclusive to the RTX 50 Series lineup. Previously, the RTX 40 Series cards were capable of frame generation. Using that, gamers were able to experience smoother gameplay. This was done by adding an artificially generated frame between two rendered frames.
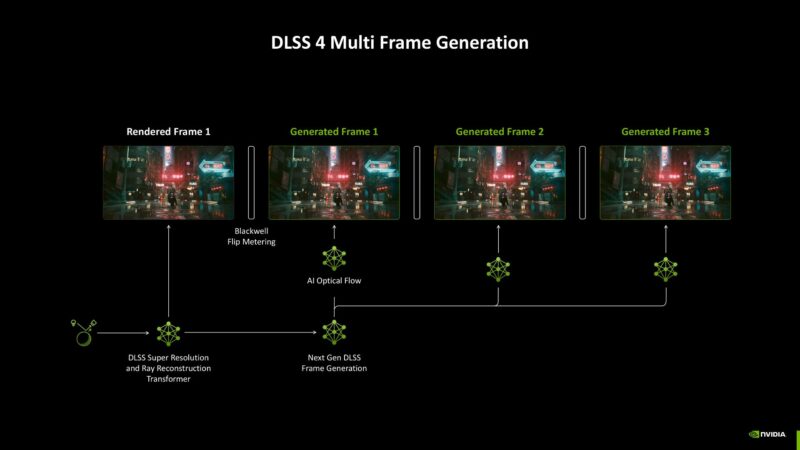
Nvidia made this possible with the help of an optical flow accelerator, which was used to predict how the generated frame would look like. Interestingly, by using multi-frame gen., it has become possible to add up to three artificial frames between two rendered frames. Not only are there more frames being generated, it is being done more quickly. Multi-frame gen. usage gives the illusion of unmatched smoothness while gaming.
A new hardware flip metering system was developed to improve video game visual output smoothness. This technology operates with more efficient frame generation algorithms to enable multi-frame generation.
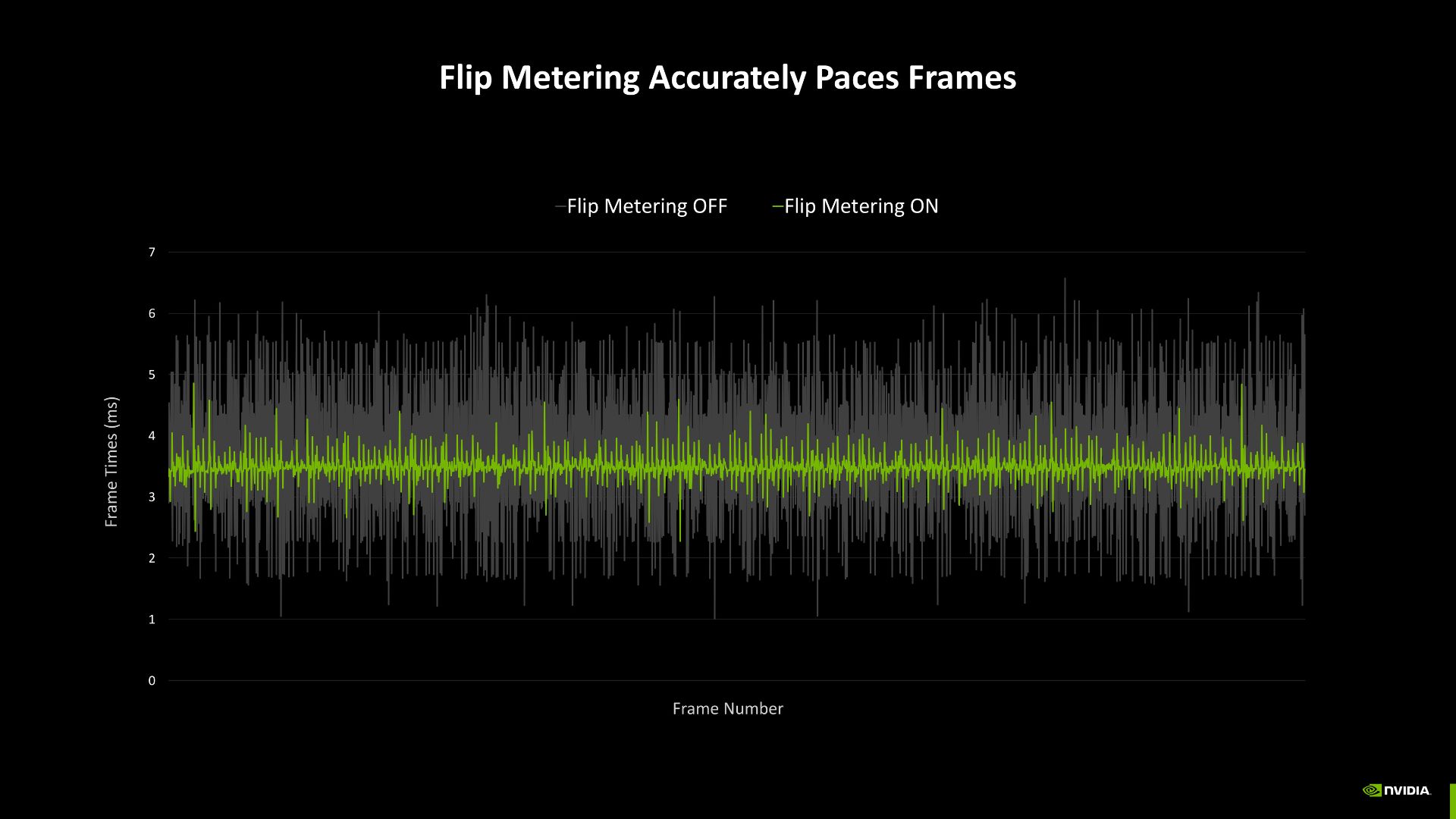
Unfortunately, this approach creates an additional problem. The effective sampling rate decreases by 25% because of this process. Games operating at predefined frame rates experience actual rendering at lower rates, but multi-frame gen. technology quadruples the output to match the specified frame rate.
This configuration delivers outstanding results under specific conditions, yet it carries risks that require cautionary attention. When hardware combined with game performance fails to reach the desired frame rate, the situation becomes hard to manage. When working with an inferior system, the maximum achievable frame rate becomes much lower.
The fundamental problem originates from the minimum performance criteria needed to generate acceptable gaming experiences. The gameplay demands a specific minimum performance level which becomes clear through comparisons with DLSS 3 Frame Generation.
Game performance must surpass specific thresholds in order to deliver fully smooth and immersive experiences. Multi-frame generation provides useful advancements, yet its success depends fundamentally on hardware systems reaching designated performance benchmarks.
Reflex 2: Nvidia’s Solution to Increased Input Lag
Generally speaking, higher framerates translate to a lower input lag. However, we can observe higher latencies when using frame generation technology to boost framerates. While it is rather easy to view the increase in FPS, due to increased input lag, the feel of it is going to be pretty much the same. Although, this wasn’t a huge problem when it came to story games, it couldn’t be ignored while playing competitive games.
Every millisecond counts in competitive gaming. When it comes to fast-paced action shooters, the higher the input latency there is, the worse your experience is going to be. If you use frame generation while playing such games, you will notice that the time between your actions and the system’s response will go up.
This is why gamers are discouraged from enabling frame generation while playing games like Marvel Rivals. However, when it comes to games like God of War Ragnarök or Black Myth: Wukong, they are not released focused on fast responses by gamers.
Moreover, input latency varies depending on the GPU in use. This is the reason why Nvidia introduced Reflex. With Reflex, Nvidia’s aim is to take out as much latency as possible from the pipeline and speed things up. The difference between input latencies of frame generation and multi-frame generation is negligible.

Nvidia created Refresh 2 designed only for RTX GPUs specifically to enhance gaming performance. They will release it originally for RTX 50-series GPUs before supporting all RTX GPUs. This updated technology outperforms Reflex by offering enhanced management of input sampling together with advanced rendering capabilities.
One key feature of Reflex 2 enables the system to predict camera movements before beginning its rendering process. Reflex 2 analyzes historical and present input data to determine camera destination points according to player movements. The system determines that the camera will move by three degrees based on its analysis of two-degree view adjustments across the last two input samples.

After finishing rendering Reflex 2 retrieves fresh input data which allows it to perform frame warping and achieve higher accuracy. The system readjusts positions which reveals hidden objects. The final image enhancement process in Reflex 2 depends on a fast AI in-painting algorithm, which fills and improves areas affected by camera warping.
Reflex 2 operates according to the frame rate performance level that games maintain. The technology delivers its peak performance during high FPS scenarios. Visual artifacts and discrepancies will increase when game framerates remain below normal levels. The initial optimization phase of Reflex 2 centers on The Finals and Valorant because competitive shooters demand precise action and fast reactions for success in matches.

Should You Get an RTX 50 Series GPU?
When considering whether to upgrade to the RTX 50 Series GPUs, it is important to account for a few factors. If you are experiencing a performance bottleneck while playing games, naturally, upgrading to a new GPU is a tempting option. However, when you are dealing with performance issues while using heavily-taxing settings like path tracing, it becomes increasingly important to consider an upgrade.
Another thing to keep in mind while upgrading to an RTX 50 Series GPU is that you are going to need a compatible motherboard as well as a PSU powerful enough to run it. You might also need to invest in a CPU, considering there are a lot of CPU-intensive games out there.
Once you have considered these factors and whether you are ready to adjust to them, you can make a solid decision on whether you should get an RTX 50 Series GPU in 2025.
Looking For More?
Thank you for reading the article. We provide the latest news and create guides for Baldur’s Gate 3, Starfield, ARK Survival Ascended, and more. Also, watch Deltia play games on Twitch or visit his YouTube channel!
 Reddit
Reddit
 Email
Email